This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
When a pathogen sweeps through a conventional farm, the immediate response often involves reaching for synthetic fungicides or bactericides, treating the symptom while the underlying vulnerability remains. Organic disease control flips this paradigm entirely, working from the soil up to create conditions where diseases struggle to gain a foothold in the first place.
By strengthening the complex web of beneficial microbes, optimizing plant nutrition, and designing resilient ecosystems, you’re not just managing diseases—you’re building living systems that naturally suppress them. This approach requires understanding how pathogens behave, recognizing early warning signs in your crops, and deploying strategic interventions that work with nature’s own defenses rather than against them.
The most effective organic growers don’t wait for problems to appear; they cultivate conditions where healthy plants can resist infection, and when disease pressure does increase, they respond with targeted biological controls and cultural practices that address root causes.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Principles of Organic Disease Control
- Identifying Common Plant Diseases
- Preventive Strategies in Organic Gardening
- Organic Methods for Disease Management
- Effective Application and Compliance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is apple cider vinegar a fungicide?
- How to control plant diseases organically?
- Is cinnamon a natural fungicide for plants?
- What is an example of an organic fungicide?
- What is organic disease management?
- What are the 5 principles of plant disease control?
- What is an organic fungicide?
- How much do organic treatments cost?
- When should organic fungicides be applied?
- Can organic methods work in greenhouses?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Organic disease control builds resilience from the soil up by strengthening beneficial microbes, optimizing plant nutrition, and creating conditions where pathogens struggle to establish rather than reacting to symptoms with synthetic chemicals.
- Prevention through crop rotation, compost-enriched soil health, sanitation practices, and disease-resistant varieties forms your strongest defense, eliminating threats before they take root and reducing reliance on external interventions.
- When diseases do appear, you’ll deploy biological control agents like Trichoderma and Bacillus species alongside organic-approved sprays such as neem oil, copper treatments, and potassium bicarbonate, timing applications according to weather patterns and disease forecasting tools.
- Maintaining organic certification requires choosing NOP-compliant inputs, documenting all treatments for five years, and passing annual third-party audits that verify your disease management strategies align with prohibited substance lists and buffer zone protocols.
Principles of Organic Disease Control
Organic disease control flips the script on conventional farming by prioritizing prevention over reaction, building resilient ecosystems that naturally resist pathogens. Instead of relying on synthetic chemicals that can harm beneficial organisms and soil health, you’ll work with nature’s own defense mechanisms to keep your crops thriving.
Start by transforming your soil with organic pest control methods that boost beneficial microbes and create naturally resistant plants from the ground up.
Understanding these foundational principles will equip you with the knowledge to protect your plants while maintaining certification standards and ecological balance.
Core Concepts and Preventive Focus
Organic disease control starts with a simple truth: healthy plants don’t get sick as often. You’re building resilience from the ground up, relying on soil microbes, plant health and protection, and integrated farming instead of quick chemical fixes. Disease ecology teaches us that prevention beats cure every time.
Organic disease control builds resilience from the ground up—healthy plants resist sickness when you prioritize prevention over chemical fixes
Here’s what organic principles demand:
- Strengthen soil life first – diverse microbial communities outcompete pathogens and improve nutrient cycling naturally.
- Catch problems early – regular scouting lets you respond before disease spreads.
- Reduce plant stress – balanced water, nutrients, and spacing keep defenses strong.
- Embrace diversity – crop rotation and polycultures disrupt pathogen life cycles while supporting plant resilience.
This preventive focus in disease management transforms how you think about fungal disease management and microbial disease control, shifting from reaction to proactive care.
Differences From Chemical-Based Methods
Unlike synthetic pesticides that promise instant knockdown, organic disease control prioritizes prevention strategies and natural resistance over reactive eradication. You’re working with biological control agents and living systems instead of harsh chemicals, timing interventions based on plant health rather than rigid schedules.
Integrated pest management and sustainable practices create resilient ecosystems where diverse approaches reduce pathogen adaptation, while organic regulations guarantee you’re using only approved inputs that support sustainable agriculture and long-term fungal disease management.
Advanced identification techniques such as are rapidly advancing how growers understand and manage plant diseases.
Role in Sustainable Agriculture
When you build disease resistance through soil health and biodiversity management, you’re investing in sustainable agriculture that protects ecosystems for generations. Organic disease control reduces chemical runoff, bolsters pollinators, and strengthens climate resilience through eco-friendly farming practices that combine integrated pest management with biological control and environmental stewardship.
- Soil conservation through composting and cover crops interrupts pathogen cycles while building carbon-friendly systems
- Biodiversity management creates habitat for beneficial organisms that suppress diseases without synthetic inputs
- Reduced chemical reliance protects aquatic ecosystems and prevents resistance development in pathogens
- Sustainable practices lower production costs while commanding premium prices in certified organic markets
- Knowledge networks accelerate adoption of proven strategies that deliver reliable crop health and profitability
To further improve farm sustainability, growers can implement such as water conservation and soil health improvement.
These methods not only protect the environment but also boost productivity, especially when paired with proven techniques for maximizing crop yield like crop rotation and precision fertilization.
Identifying Common Plant Diseases
You can’t fight what you can’t see, and understanding the enemy is your first line of defense in organic disease control. Plant diseases fall into three main categories based on their causative agents, each with distinct symptoms and transmission methods that require different management approaches.
Recognizing whether you’re dealing with bacteria, fungi, or viruses will determine your entire control strategy and protect your crops before damage becomes irreversible.
Recognizing Bacterial Diseases
Bacterial identification begins with observing leaf spot symptoms, particularly water-soaked halos and yellow rings surrounding lesions. When you suspect bacterial infection, cut stems to check for rapid vascular browning under magnification.
Watch for soft rots releasing foul odors as tissue decays, and note that bacteria spread through tools, hands, and rain splash.
Proper plant diagnosis is essential for effective disease management in organic farming.
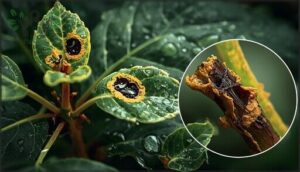
Spotting Fungal Infections
Fungal identification starts with examining leaf spot patterns—look for concentric rings, black spore specks, or irregular lesions with yellow halos. Powdery mildew leaves a white coating you can brush off, while rust diseases create orange pustules that rub onto your fingers.
High humidity and poor airflow trigger fungi like Rhizoctonia, Fusarium, and Pythium, making early detection critical before fungicide application becomes necessary.
Understanding Viral Plant Diseases
Viruses pose unique challenges because they hijack plant cells to replicate, spreading through vectors like aphids, whiteflies, and even contaminated tools. Unlike bacterial or fungal pathogens, viral symptoms appear as mosaics, curling, and stunted growth—damage that’s irreversible once infection takes hold.
- Virus transmission occurs when insects feed on infected tissue, then move to healthy plants
- Plant vectors like leafhoppers expand disease epidemiology across your garden rapidly
- Viral symptoms include distinctive ring patterns and chlorosis requiring careful observation
- Host resistance varieties offer your strongest defense in disease management
- Remove infected plants immediately—organic methods can’t cure viruses, only prevent spread
Preventive Strategies in Organic Gardening
Prevention stands as your strongest line of defense in organic gardening, eliminating disease threats before they take root in your crops. By focusing on proactive measures rather than reactive treatments, you create a growing environment where plants naturally resist infection and thrive without chemical intervention.
The following strategies form the foundation of effective disease prevention, each addressing a critical component of plant health and resilience.
Crop Rotation and Plant Diversity
Rotating your crops breaks disease cycles by shifting host plants each season, reducing pathogen pressure and balancing soil nutrients over time. In Organic Farming, this approach to Sustainable Agriculture strengthens Soil Health through Soil Renewal, builds resilience against pests, and lowers your reliance on external inputs.
Crop Planning and Rotational Design increase Plant Diversity, encouraging beneficial soil organisms that support Ecological Balance and Biodiversity Benefits.
Enhancing Soil Health With Compost
You can transform your soil into a living shield against disease by adding compost rich in Organic Matter that fuels Soil Microbes and accelerates Nutrient Cycling. Compost Benefits extend beyond feeding plants—they build soil health through microbiotic activity that outcompetes pathogens:
- Humus Formation improves structure and moisture retention
- Diverse organic fertilizers stimulate beneficial soil microbiology
- Enhanced cation exchange capacity holds nutrients longer
- Microbial respiration suppresses soil-borne diseases
- Earthworm activity aerates and enriches the root zone
Sanitation and Removing Infected Plants
Once Disease Management begins, your first line of defense is swift Debris Removal and Field Hygiene—both safeguard crops from further infection. Bag and dispose of symptomatic tissue immediately, sanitize tools with 70 percent alcohol between cuts, and enforce Post Removal Protocols that include area disinfection and neighboring plant inspection. These Organic Methods in Plant Pathology prevent pathogen spread and restore control.
| Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Remove infected material promptly | Halt inoculum spread |
| Disinfect tools between plants | Prevent cross contamination |
| Clean surrounding area after removal | Reduce residual pathogens |
Selecting Disease-Resistant Varieties
You gain the upper hand when you choose varieties bred for resistance to fungi, bacteria, and viruses common in your region. Resistance Breeding and Variety Selection give you Resistant Cultivars with documented Disease Tolerance, reducing reliance on sprays and strengthening Crop Improvement through Genetic Diversity.
Certified seeds carry labeled resistance traits—match them to local disease pressure for effective Disease Control and smarter Disease management in organic farming rooted in Plant pathology principles.
Organic Methods for Disease Management
Once you’ve laid the groundwork with prevention, you’ll need tools to manage diseases when they do appear.
Organic disease management relies on biological controls, targeted treatments, and strategic practices that work with nature rather than against it.
Here’s how you can protect your crops without compromising your organic principles.
Biological Control Agents and Beneficial Organisms
You can employ biological control agents to suppress pathogens without synthetic chemicals, reclaiming your farm from disease pressure. Microbial control through Trichoderma and Bacillus species inhibits fungal growth, while beneficial insects like lady beetles and lacewings reduce pest-vectored infections.
Nematode management targets soil-dwelling larvae, and natural predators maintain ecological balance. Soil ecology thrives when you integrate these biological controls, building long-term resilience against recurring plant diseases.
Organic-Approved Sprays and Treatments
You’ll expand your biological control strategy with organic sprays that target specific threats on your terms. Neem oil disrupts soft-bodied pests, while copper spray and potassium bicarbonate suppress fungal diseases.
Horticultural oil smothers insect eggs, kaolin clay forms a protective barrier on leaves, and Bacillus spray eliminates caterpillars with precision.
These organic pest control methods put you in command of disease management without compromising certification.
Physical Barriers and Cultural Practices
You command the growing environment with row covers and mulching techniques that block pathogen contact, while crop spacing and airflow management dry foliage faster after rain. Soil sanitation through tool disinfection and crop rotation breaks disease cycles between seasons.
These physical barriers and cultural practices form your first line of defense, strengthening soil health and complementing biological controls in organic farming methods.
Companion Planting and Habitat Conservation
Companion planting fosters biological controls by attracting natural predators through pollinator gardens and biodiversity conservation, creating ecological balance across your organic farming system.
Plant flowering companions alongside crops to establish wildlife corridors that sustain beneficial insects throughout the season, while habitat restoration through diverse plantings strengthens sustainable agriculture and reinforces the physical barriers you’ve already implemented.
Effective Application and Compliance
You can master organic disease control methods, but none of that matters if you don’t apply them correctly or stay compliant with organic standards. The difference between success and failure often comes down to choosing the right inputs, timing your applications properly, and keeping thorough records that satisfy certification requirements.
Let’s break down the essential practices that will keep your organic operation both effective and fully compliant.
Choosing NOP-Compliant Inputs
You’ll want to verify that every product you select carries official organic certification and appears on the National Organic Program’s approved inputs list, confirming supplier certification before purchase.
Proper organic labeling and documentation protect you from compliance risks while supporting sustainable sourcing aligned with organic methods for disease control, natural pest control, and integrated pest management strategies essential to maintaining your organic certification status.
Proper Application Timing and Techniques
Timing your applications according to disease forecasting tools and weather patterns ensures maximum effectiveness while minimizing waste, making spray volume optimization and equipment calibration methods essential components of disease management in organic farming. Integrated pest management relies on precise foliar spray techniques and application window timing to coordinate biological controls with cultural practices for complete disease control using organic methods.
- Apply protectants before predicted leaf wetness or high humidity fronts to intercept infection periods
- Use 200 to 400 liters per hectare for dense canopies to achieve thorough coverage on both leaf surfaces
- Schedule treatments in early morning or late afternoon to reduce leaf burn and water loss on hot days
- Maintain proper nozzle angle and height to create uniform droplet size suitable for your target disease
- Reapply every 7 to 14 days depending on rainfall and leaf wetness duration to maintain protection
Monitoring, Record Keeping, and Adjustments
Vigilance keeps your disease management strategies sharp. Daily disease surveillance paired with consistent record management lets you track symptom density, correlate soil health scores with outbreak patterns, and deploy adjustment strategies when infection risk crosses defined thresholds.
Data analysis transforms field observations into actionable insights for crop disease control, while compliance verification through timestamped logs ensures your organic methods meet documentation standards and support effective disease management in organic farming.
Meeting Organic Certification Standards
Organic certification transforms your disease control practices into verifiable sustainable agriculture. The certification process demands that you align input management, farm planning, and compliance verification with National Organic Program standards, ensuring your organic methods meet strict requirements from soil amendments to pest controls.
- Third-party certifiers audit your practices against organic farming standards annually
- Documentation must trace approved inputs and disease control treatments for five years
- Organic labels require compliance with prohibited substance lists and buffer zone protocols
- Annual inspections verify that your strategies support both crop health and certification renewal
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is apple cider vinegar a fungicide?
Apple cider vinegar shows limited fungicide activity through its acetic acid content, which inhibits some fungal growth on contact.
However, it’s not a reliable broad-spectrum solution compared to certified organic fungicides and integrated disease control strategies.
How to control plant diseases organically?
Think of your garden as an ecosystem where balance beats brute force. You’ll control plant diseases organically by rotating crops, enriching soil with compost, deploying beneficial microbes, applying organic fungicides, and choosing disease-resistant varieties.
Is cinnamon a natural fungicide for plants?
Yes, cinnamon acts as a natural fungicide because its cinnamaldehyde disrupts fungal cell processes, reducing damping off in seedlings and slowing Botrytis growth.
Though it works best as prevention rather than treating established infections.
What is an example of an organic fungicide?
You’ll find copper sulfate mixed with lime, forming Bordeaux mix, coating plant surfaces to denature fungal proteins and prevent spore germination.
This is a classic choice alongside neem oil and potassium bicarbonate sprays for managing fungi organically.
What is organic disease management?
Organic disease management combines prevention, soil biology, and integrated management to suppress plant diseases without synthetic chemicals.
You’ll use eco-friendly methods like biological control, crop rotation, and beneficial microbes to build long-term resilience in your growing system.
What are the 5 principles of plant disease control?
Disease control follows five core principles: avoidance tactics, eradication methods, protection strategies, host resistance, and therapy approaches.
You’ll find these principles in both conventional and organic methods, though execution differs markedly.
What is an organic fungicide?
Natural fungicides derived from minerals, plants, or microorganisms control fungal infections while meeting organic certification standards.
Examples include sulfur, copper-based products, neem oil, and biofungicides containing beneficial microbes that protect your crops without synthetic chemicals.
How much do organic treatments cost?
Prices swing from $12 insecticidal soaps to $60 biological applications, varying by region and pest pressure—but healthier soils eventually slash input needs by 20 to 40 percent, rewarding your patience.
When should organic fungicides be applied?
You’ll get the best results by applying organic fungicides at the first sign of disease or when weather forecasting predicts high pressure, scheduling spray applications every seven to fourteen days during active growth.
Can organic methods work in greenhouses?
You can absolutely succeed with organic methods in greenhouse microclimates by combining disease forecasting, greenhouse sanitation, soil temperature management, and biological controls—creating sustainable agriculture systems that outperform conventional approaches while controlling organic pests naturally.
Conclusion
The strongest defense against disease isn’t a spray bottle—it’s the soil beneath your feet, the diversity in your planting plan, and your commitment to observing what your crops are telling you.
Organic disease control demands vigilance and a willingness to work with ecological processes rather than override them, but the payoff is a farm or garden that becomes more resilient with each season, requiring less intervention as natural balance takes hold.